


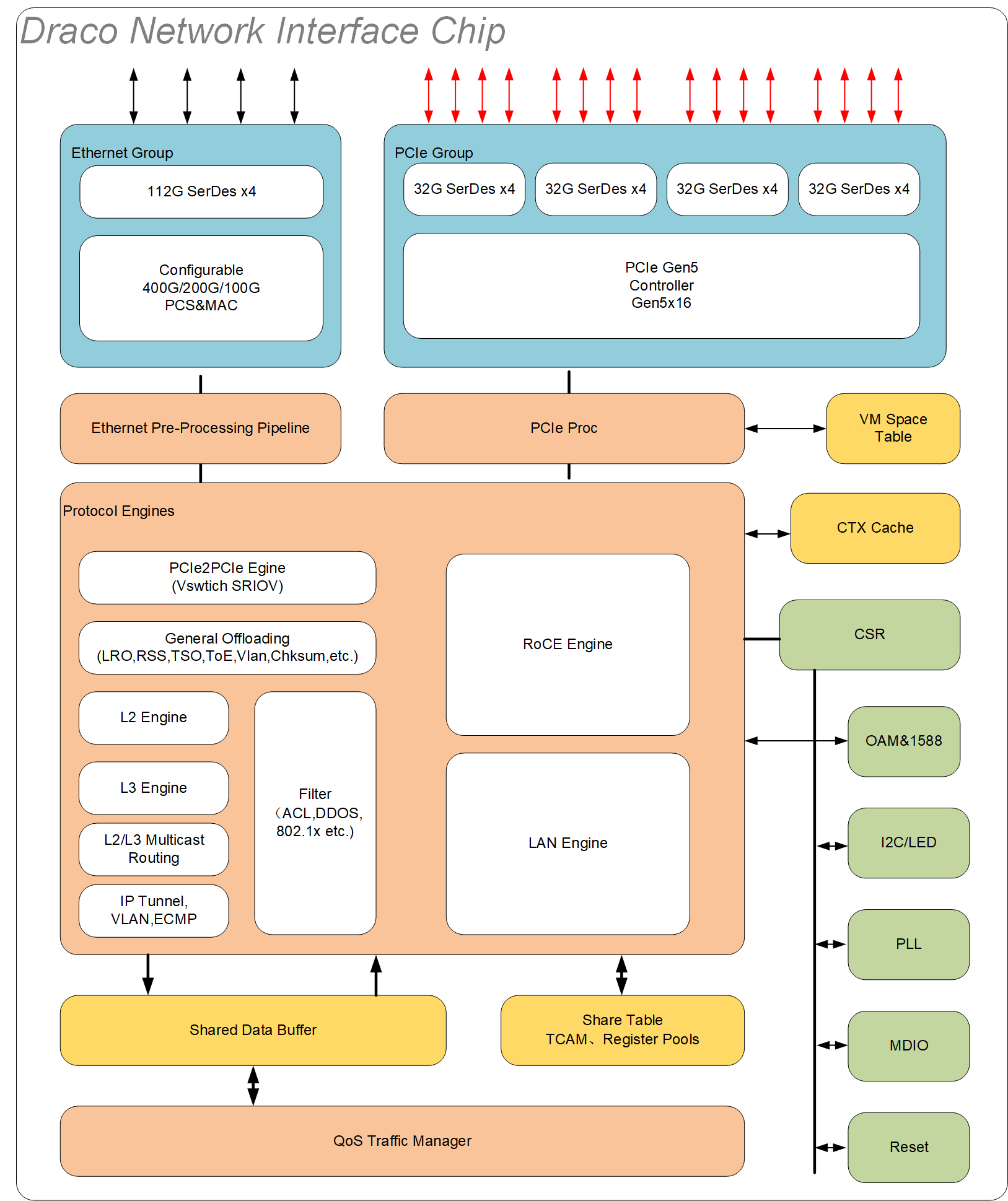
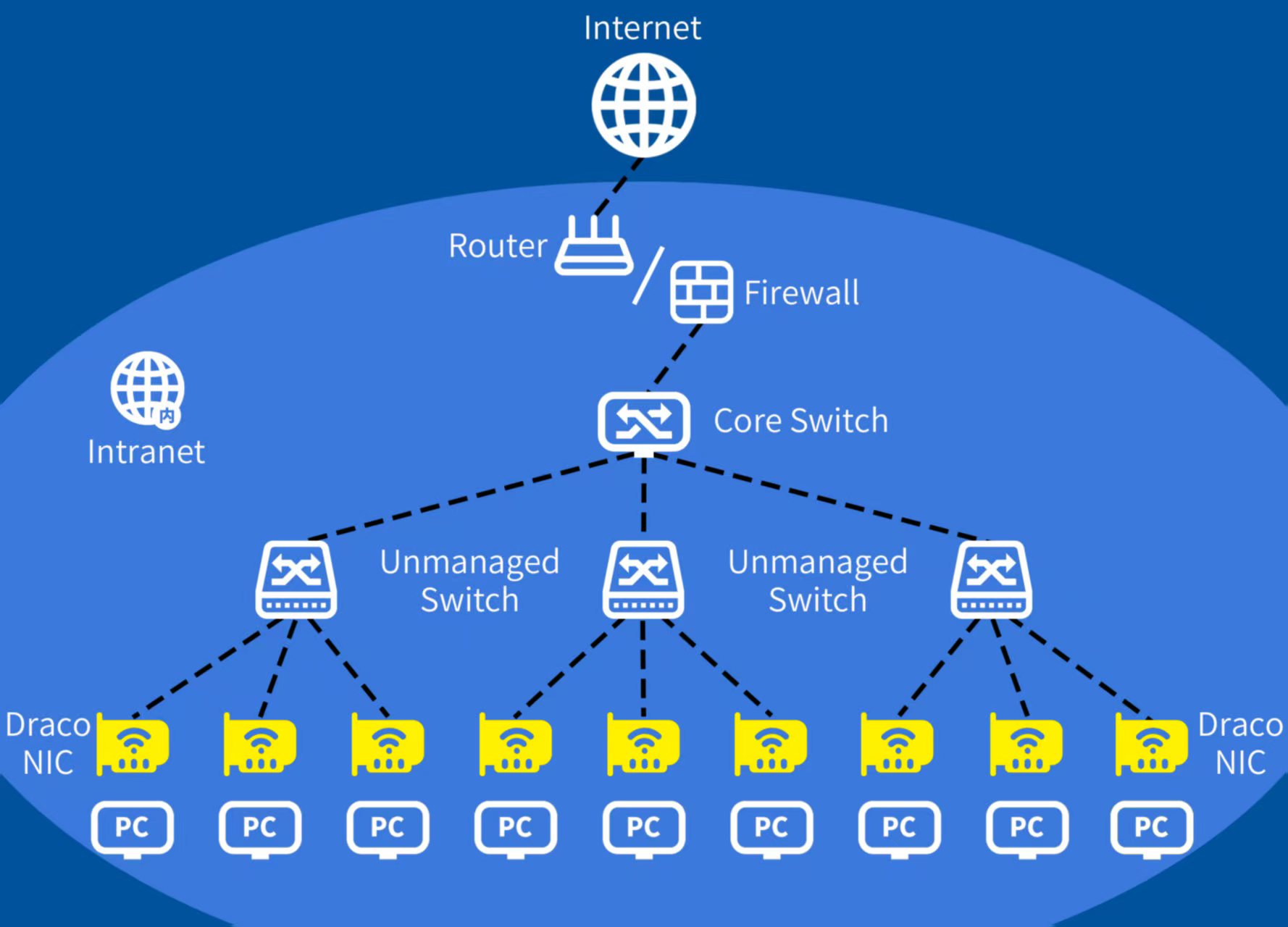
The Draco chips may play a critical role in modern enterprise networks by specializing in ultra-low-latency data processing and real-time decision-making.
- Consumer Electronics: mobile phones, tablets, smart home devices (Wi-Fi/Bluetooth/Ethernet chips).
- PCs & Servers: Chips in network interface cards (NICs) (e.g., Intel 82599, Marvell Alaska).
- Industrial Equipment: PLCs and sensors connected via industrial Ethernet protocols (e.g., PROFINET).

- Data Centers: High-speed Ethernet chips (25G/100G/400G) in server NICs (e.g., Broadcom BCM574xx series).
- Storage Systems: RDMA-enabled NICs (e.g., Mellanox ConnectX) for NVMe-over-Fabrics (NVMe-oF) storage devices.

- In-Vehicle Networks: Automotive Ethernet chips (e.g., NXP SJA1105) for ADAS and infotainment systems.
- 5G Base Stations: FPGA or ASIC chips handling fronthaul (eCPRI) and backhaul traffic.

- Low-power chips (e.g., TI CC series) for NB-IoT, LoRa, and other wireless connectivity.
